The Patient’s Guide to Podiatric Surgery: Expectations and Outcomes
November 8, 2023
Unlocking Mobility: The Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Laminectomy Procedures
December 14, 2023Revolutionizing Spinal Treatment: Kyphoplasty Through the Lens of Orthopedic Expertise
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is used to treat vertebral compression fractures, which are most commonly caused by osteoporosis, cancer, or injury. This procedure is performed by orthopedic specialists, who are medical doctors trained in the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and rehabilitation of disorders, injuries, and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. This article will provide an in-depth look at kyphoplasty, the role of orthopedic specialists in performing this procedure, and the associated benefits and risks.
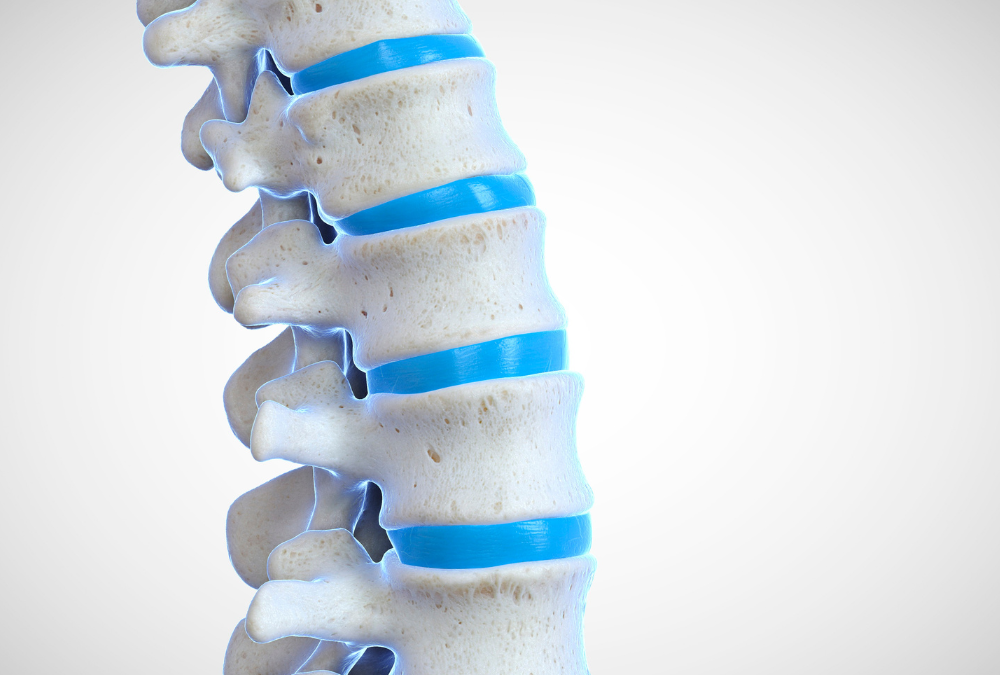
The term ‘kyphoplasty’ is derived from the Greek words ‘kyphos’ meaning hump and ‘plasty’ meaning molding or forming. The procedure is designed to restore the normal shape and size of the spine and alleviate pain caused by vertebral compression fractures. It involves the insertion of a small balloon into the fractured vertebra, which is then inflated to create a space. This space is then filled with a special cement to stabilize the fracture.
Understanding Vertebral Compression Fractures
Vertebral compression fractures occur when the vertebral body in the spine collapses, which can lead to severe pain, deformity and loss of height. These fractures more commonly occur in the thoracic spine (the middle portion of the spine), especially in the lower part. Osteoporosis, a disease that results in a decrease in the density and quality of bone, is the most common cause of this type of fracture.
Other causes of vertebral compression fractures include trauma such as a fall or motor vehicle accident, or pathological fractures due to cancer or infection. Symptoms of a vertebral compression fracture can include sudden onset of back pain, pain that worsens when standing or walking, loss of height, deformity of the spine and limited spinal mobility.
Diagnosis of Vertebral Compression Fractures
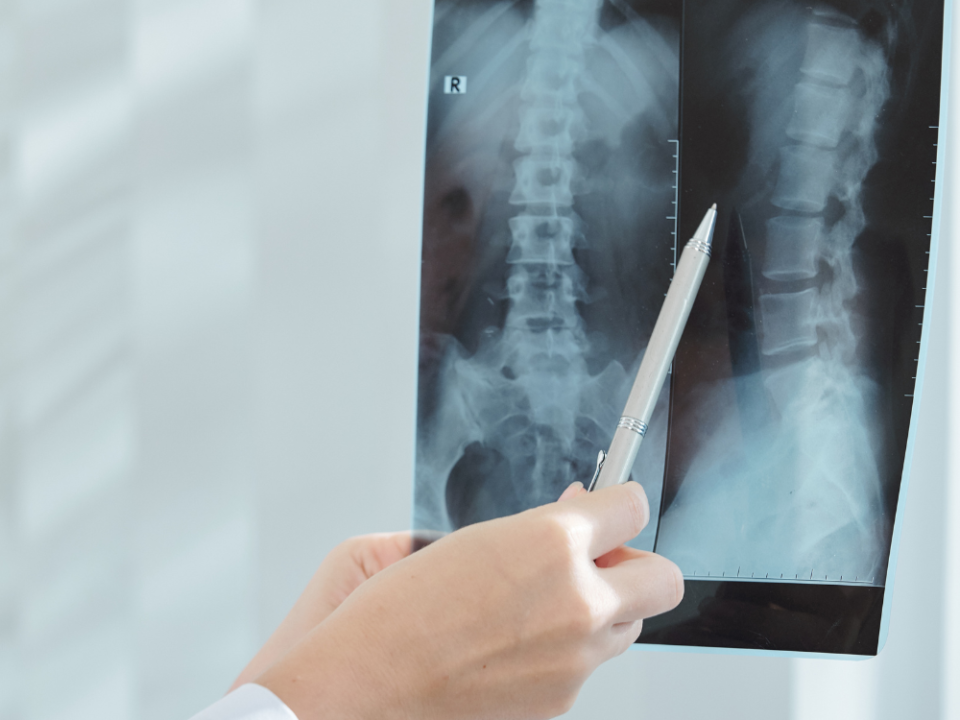
Orthopedic specialists use a variety of diagnostic techniques to identify vertebral compression fractures. These techniques include physical examinations, during which the doctor will look for signs of pain, tenderness, or deformity on palpation of the back, and neurological examinations to check for signs of nerve damage or other complications.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are also commonly used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the fracture. In some cases, a bone density test may also be performed to determine if osteoporosis is the underlying cause of the fracture.
The Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Kyphoplasty
Orthopedic specialists play a crucial role in the performance of kyphoplasty procedures. These medical professionals have extensive training and experience in managing musculoskeletal disorders, including vertebral compression fractures. They are responsible for assessing the patient’s condition, determining the appropriateness of kyphoplasty, performing the procedure, and managing the post-operative care.
Orthopedic specialists work in a multidisciplinary team that includes anesthesiologists, nurses, and physical therapists. They use their expertise in anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics to ensure the procedure is performed accurately and safely. They also play a key role in patient education, explaining the procedure, its risks and benefits, and the expected recovery process to the patient.
Training and Education of Orthopedic Specialists
Orthopedic specialists undergo rigorous training and education to acquire the skills and knowledge necessary to perform procedures like kyphoplasty. This typically includes four years of undergraduate studies, four years of medical school, and a five-year residency in orthopedic surgery. Some orthopedic specialists also choose to complete additional fellowship training in a specific area of orthopedics, such as spine surgery.
Throughout their training, orthopedic specialists learn about the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions. They gain hands-on experience in surgical techniques, patient care, and the management of orthopedic problems. They also learn about the latest research and advancements in the field of orthopedics.
The Kyphoplasty Procedure
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that is typically performed under local or general anesthesia. The patient is positioned face down, and a small incision is made in the back over the affected vertebra. Using X-ray guidance, the orthopedic specialist inserts a narrow tube through the pedicle into the fractured vertebra.
A special balloon is then inserted through the tube and into the vertebra. The balloon is inflated to create a cavity or space in the bone. Once the space has been created, the balloon is deflated and removed, and the cavity is filled with a bone cement to stabilize the fracture. The cement hardens quickly, providing immediate stability to the vertebra and helping to alleviate pain.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After the kyphoplasty procedure, patients are typically observed in a recovery room for a few hours before being discharged home. Pain at the site of the procedure is common but is usually mild and can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications. Most patients are able to return to their normal activities within 24 hours of the procedure.
Orthopedic specialists play a key role in the post-procedure care of patients who have undergone kyphoplasty. They provide instructions for home care, prescribe medications for pain control, and recommend physical therapy exercises to improve mobility and strength. They also schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the patient’s recovery and ensure the success of the procedure.
Risks and Benefits of Kyphoplasty
Like all surgical procedures, kyphoplasty carries some risks. These can include infection, bleeding, increased back pain, and complications related to anesthesia. There is also a small risk that the bone cement can leak out of the vertebra and into the surrounding tissues or blood vessels, which can cause serious complications.
However, when performed by experienced orthopedic specialists, kyphoplasty is generally a safe and effective procedure. It can provide immediate pain relief and help restore normal spine alignment and height. It can also improve mobility and quality of life for patients with vertebral compression fractures.
Considerations for Kyphoplasty
Not all patients with vertebral compression fractures are candidates for kyphoplasty. The procedure is typically recommended for patients who have severe pain that is not relieved by conservative treatments such as rest, pain medications, and bracing. It is also used for fractures that have led to significant spinal deformity or loss of height.
Orthopedic specialists carefully consider a variety of factors before recommending kyphoplasty. These include the patient’s overall health, the location and severity of the fracture, the presence of any underlying conditions such as osteoporosis or cancer, and the patient’s personal preferences and expectations.
Conclusion
Kyphoplasty is a valuable tool in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. This minimally invasive procedure can provide significant pain relief and improve quality of life for patients suffering from these fractures. Orthopedic specialists play a crucial role in the performance of this procedure, from the initial diagnosis and treatment planning to the post-operative care and recovery.
As with any surgical procedure, it is important for patients to understand the risks and benefits of kyphoplasty and to discuss these with their orthopedic specialist. With the right information and care, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and work towards a successful recovery.