Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Overview
January 16, 2024
Enhancing Hand Function: A Comprehensive Guide to MP Joint Health in Orthopedics
February 12, 2024The Role of Physical Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects around 1.3 million adults in the United States alone. It is characterized by inflammation in the lining of joints, which can lead to pain, stiffness, and decreased joint mobility. While there is no cure for RA, there are various treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. One such treatment modality is physical therapy, which plays a crucial role in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. At Center For Specialty Care, our skilled and highly trained physical therapists will help you along this journey!
How Physical Therapy Can Improve Joint Mobility in RA
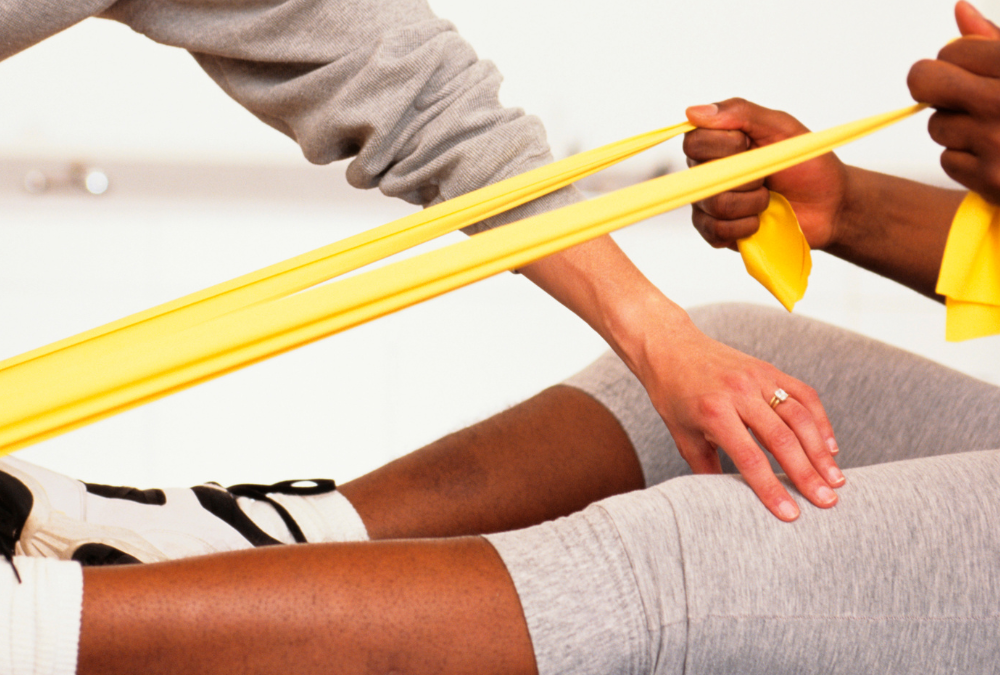
Physical therapy is essential in improving joint mobility for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can significantly impact a person’s ability to move and perform daily activities. However, with the help of physical therapy, individuals with RA can regain and maintain their joint mobility, improving their overall quality of life.
Through targeted exercises and stretching techniques, physical therapists can help patients increase their range of motion, reducing joint stiffness and allowing for better movement. These exercises are designed to specifically target the affected joints, helping to improve their flexibility and function. By gradually increasing the intensity and duration of these exercises, physical therapists can help patients achieve significant improvements in their joint mobility over time.
Regular physical therapy sessions can also help prevent muscle and joint contracture, which can result from prolonged immobility and worsen RA symptoms. Contracture occurs when the muscles and tendons around a joint become tight and shortened, leading to a loss of motion and increased pain. Physical therapists can use various techniques, such as manual therapy and stretching exercises, to prevent and treat contracture in individuals with RA.
During physical therapy, therapists may incorporate a variety of exercises, such as gentle range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and aerobic exercises. Range-of-motion exercises involve moving the affected joints through their full range of motion, helping to maintain their flexibility and prevent stiffness. Strengthening exercises, on the other hand, focus on improving the strength of the muscles around the joints, providing better support and stability. These exercises can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities, ensuring a safe and effective treatment plan.
In addition to exercises, physical therapists may also use other modalities to improve joint mobility in individuals with RA. These may include heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and hydrotherapy. Heat therapy can help relax the muscles and increase blood flow to the affected joints, promoting healing and reducing pain. Cold therapy, on the other hand, can help reduce inflammation and swelling, providing temporary relief from RA symptoms.
Ultrasound and electrical stimulation are modalities that can be used to reduce pain and promote tissue healing. Ultrasound uses sound waves to generate heat deep within the tissues, helping to increase blood flow and relax the muscles. Electrical stimulation, on the other hand, uses electrical currents to stimulate the nerves and muscles, providing pain relief and improving muscle function.
Hydrotherapy, or water therapy, is another effective modality used in physical therapy for individuals with RA. The buoyancy of water helps reduce the impact on the joints, allowing for easier movement and exercise. Hydrotherapy can also provide gentle resistance, helping to strengthen the muscles without putting excessive stress on the joints.
Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving joint mobility in individuals with RA. By incorporating a combination of targeted exercises, stretching techniques, and other modalities, physical therapists can help patients regain and maintain their joint flexibility, reduce pain, and improve their overall function. It is important for individuals with RA to work closely with their physical therapists to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Exploring the Benefits of Physical Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
In addition to improving joint mobility, physical therapy offers numerous benefits for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. One of the key advantages is pain relief. Physical therapists can utilize various techniques, such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and manual therapy, to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in affected joints. By decreasing pain levels, individuals with RA can enhance their overall function and quality of life.
Furthermore, physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving muscle strength and flexibility. Rheumatoid arthritis often leads to muscle weakness and stiffness, making it difficult for individuals to perform daily activities. Physical therapists design exercise programs that target specific muscle groups, helping patients regain strength and flexibility. These exercises not only enhance physical capabilities but also promote independence and self-confidence.
Another benefit of physical therapy is the prevention of disability. RA can lead to progressive joint damage, which may eventually result in disability. However, physical therapists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that focus on slowing down the disease progression and preventing long-term disability. Through a combination of exercises, stretches, and joint protection techniques, physical therapy aims to preserve joint function and prevent further deterioration.
In addition to the physical benefits, physical therapy also provides psychological support for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Living with a chronic condition can take a toll on one’s mental health, leading to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Physical therapists not only address the physical aspects of the disease but also provide emotional support and guidance. They educate patients about coping strategies, stress management techniques, and relaxation exercises, helping them maintain a positive mindset and improve their overall well-being.
Moreover, physical therapy offers education and self-management strategies for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Physical therapists educate patients about the disease process, its impact on the body, and the importance of adhering to treatment plans. They teach self-management techniques, such as joint protection techniques, energy conservation strategies, and proper body mechanics, empowering patients to take an active role in managing their condition. By providing knowledge and skills, physical therapy enables individuals with RA to make informed decisions and effectively manage their symptoms.
In summary, physical therapy is a valuable component of rheumatoid arthritis treatment. It not only improves joint mobility and reduces pain but also prevents disability, enhances muscle strength and flexibility, provides psychological support, and offers education for self-management. By incorporating physical therapy into their treatment plan, individuals with RA can experience improved physical function, increased independence, and a better quality of life.
Tailoring Physical Therapy Interventions to Individual Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Each individual with rheumatoid arthritis experiences the disease differently. Therefore, it is crucial for physical therapists to tailor their interventions to meet the specific needs of each patient. The initial physical therapy evaluation helps identify the affected joints, assess joint stability, and determine individual goals and preferences.
Based on the evaluation, physical therapists design comprehensive treatment plans that may include a combination of exercise, manual therapy, assistive devices, and patient education. These plans are constantly adjusted and modified as the patient’s condition progresses, ensuring that they receive the most effective and personalized care throughout their journey with rheumatoid arthritis.
Pain Management Techniques in Physical Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pain management is a crucial aspect of physical therapy for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Physical therapists employ various techniques to help patients better manage their pain and improve their overall well-being.
One commonly used technique is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), where low-voltage electrical currents are applied to the skin, reducing pain signals and promoting the release of endorphins, natural pain-relieving compounds. This non-invasive approach can provide significant pain relief for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to TENS, physical therapists may also use heat or cold therapy to manage pain. Heat treatments, such as warm moist packs or paraffin wax baths, help decrease joint stiffness and ease muscle tension. On the other hand, cold therapy, like ice packs or cold compresses, can reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing temporary pain relief.
Addressing Fatigue and Energy Conservation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Rehabilitation
One of the common symptoms experienced by individuals with rheumatoid arthritis is fatigue. Fatigue can significantly impact a person’s ability to engage in daily activities and negatively affect their quality of life. Physical therapists play a vital role in addressing fatigue and teaching energy conservation techniques.
Through activity pacing, rest breaks, and proper body mechanics, physical therapists help individuals with RA learn how to conserve their energy and manage their daily activities more efficiently. This empowers patients to continue participating in activities they enjoy while minimizing exhaustion and fatigue.
Integrating Physical Therapy with Medication and Other Treatment Modalities in Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Physical therapy should be seen as an integral part of a comprehensive treatment plan for rheumatoid arthritis. When combined with medication, such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy can help maximize the benefits of these medications.
Additionally, physical therapists may collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as rheumatologists and occupational therapists, to provide a holistic approach to RA management. This collaborative effort ensures that patients receive the most comprehensive care possible, targeting all aspects of the disease and its impact on their daily lives.
How Physical Therapy Helps RA Patients
Physical therapy offers a range of benefits to individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, including:
- Improved joint mobility
- Pain relief
- Prevention of disability
- Fatigue management
- Inclusion in a comprehensive treatment plan
These benefits not only improve physical well-being but also enhance the overall quality of life for individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Setting Goals and Measuring Progress
Setting realistic goals and measuring progress are essential components of physical therapy for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Goals may include improving joint mobility, reducing pain levels, increasing daily activity levels, or improving overall function.
Physical therapists regularly evaluate and reassess patients’ progress, adjusting treatment plans as necessary. This helps ensure that patients are achieving their goals and making meaningful improvements in their daily lives. By tracking progress, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can see the tangible benefits of physical therapy and stay motivated throughout their treatment journey.
In conclusion, physical therapy has a vital role in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Through targeted exercises, pain management techniques, fatigue management strategies, and collaboration with other healthcare professionals, physical therapists can help individuals with RA improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and enhance their overall quality of life. With a personalized and comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can regain control over their lives and effectively manage the impact of this chronic condition.




